Build a lightweight on-demand image capture system using ESP32-CAM, MQTT, HTTP, & Mobile Application. In many situations, people need to check what is happening at a remote location without installing complex or expensive camera systems. Often, a simple image at...
Read More >>What Is BLE?
Bluetooth Low Energy or BLE is a wireless technology used to connect devices. Furthermore, the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (Bluetooth SIG) developed this technology focusing on industries like healthcare, security, home entertainment, etc. Moreover, the BLE is Bluetooth version 4.0 and focuses on the Internet of Things (IoT) application.
In addition, BLE is a low-power wireless technology that transmits a small amount of data at lower speeds. People use BLE in low bandwidth applications, transmitting sensor data, and controlling devices. It has low-duty data cycles and operates in a channel having a radio frequency above 40. BLE also has a quicker connection capability compared to its previous versions. Lastly, Bluetooth 5 introduced in 2016 is a modification on BLE enhancing speed, range, and data capacity.
Why BLE is used?
The Bluetooth Special Interest Group (Bluetooth SIG) designed Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), or Bluetooth 4.0, specifically for low-power applications. Moreover, it utilizes a simpler modulation system on the 2.4 GHz radio frequency band, enabling dual-mode devices to share a single radio antenna. This efficient resource use creates exceptional energy efficiency in BLE, making it ideal for battery-powered devices.
In addition, low cost and widespread adoption within the development community drive BLE’s popularity. The affordability and ease of implementation make BLE a preferred choice for a wide range of applications, particularly in the Internet of Things (IoT) domain. Furthermore, integrating BLE into smartphones further accelerated its growth by providing IoT developers with a readily accessible platform to scale their operations and create innovative connected devices.
BLE’s ability to operate in ecosystems demanding a throughput of 1 MB/s showcases its versatility. Consequently, this bandwidth capacity allows BLE to support a variety of applications, from simple sensor data transmission to more complex tasks requiring real-time data exchange.
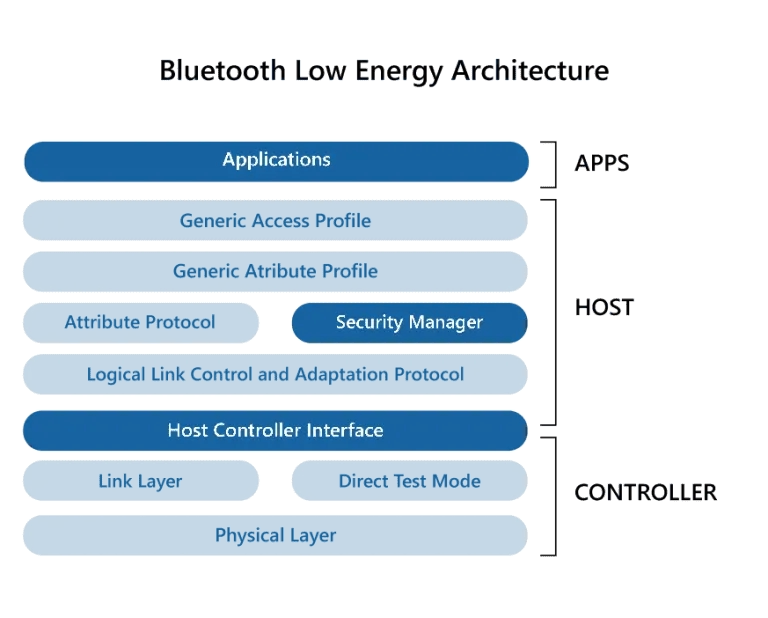
Bluetooth Low Energy Architecture

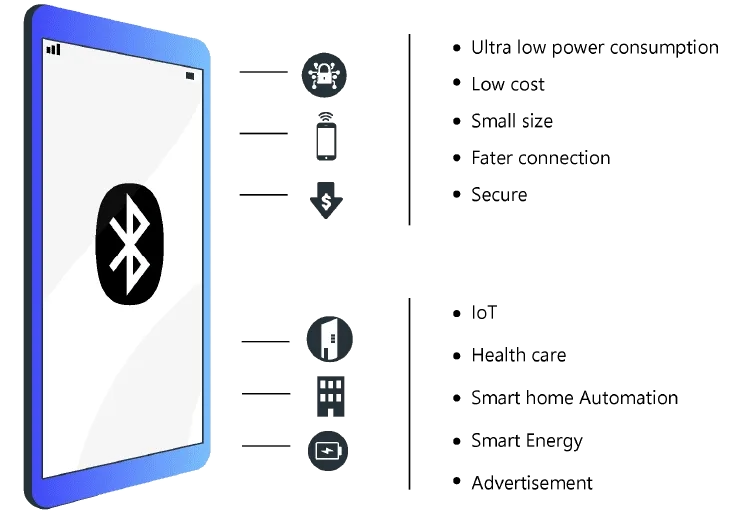

Use Cases with BLE
Connect with us to develop IoT solutions
Recent Blogs
Smart Indoor Environmental Monitoring: Detect Air Quality, Humidity, and Moisture Before Problems Begin Indoor environments can change quickly without anyone noticing. Dust levels may rise within minutes, humidity can spike during weather changes, and hidden moisture can create mold long...
Read More >>How Smart Air Mattresses Can Revolutionize Patient Comfort and Prevent Bed Sores Bed sores, also known as pressure ulcers, are injuries to the skin and underlying tissue caused by prolonged pressure on the skin. They commonly occur in patients who...
Read More >>





